Allergy
Blood Diseases
Bone & Joints
Brain
Cancer
Child Care
Cosmetic Surgery
Diabetes
Endocrinology
ENT
Eye
Gen Medicine
General Surgery
Heart
Kidney
Lifestyle
Liver & Digestive
Lung
Men’s Health
Mental health
Physiotherapy
Rheumatology
Skin and hair
Sleep Disorders
Spine
Transplant
Women Health
Thyroid
Vascular Surgery
Pap Smear
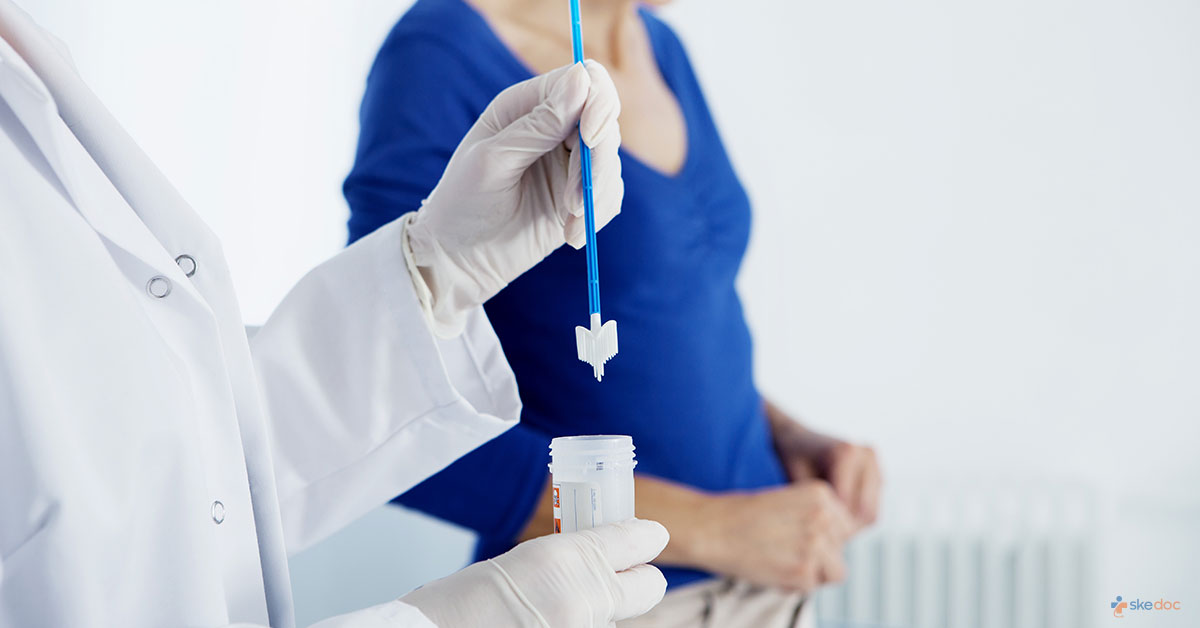
What is PAP Smear?
PAP Smear is a screening test that is done to detect cancer and precancerous conditions of the cervix through microscopic examination of the cells in the neck of the womb (cervix).
The cervix is the lowermost portion of the uterus, cylindrical in shape with an external opening in the vagina and helps in the passage of semen into the uterus.
It is a preventive test as it helps in the early detection and management of precancerous conditions, thereby preventing progression to cervical cancer.
Alternate Names
- Papanicolaou Test
- Papanicolaou smear
- PAP Test
- Cervical Smear
- Cervical Screening
- Smear Test
Is the PAP Smear procedure an elective or an emergency procedure?
PAP Smear is an elective outpatient procedure.
Indications
PAP Smear is indicated in women over the age of 21 years in sexually active women and is usually done along with a pelvic examination for the following:
- Diagnosis and detection of cancerous conditions affecting the cervix
- Diagnosis and detection of precancerous conditions affecting the cervix
Contraindications & Risk Factors
There are no absolute contraindications for performing a PAP Smear other than the following:
- During menstruation
- Presence of active vaginal/cervical infection; treatment is needed before a PAP Smear is done
Investigations before the procedure
There are no other investigations required before performing a PAP Smear.
Pre procedure advice
The following are advised before performing the test:
- Avoiding vaginal intercourse 48 hours before the test
- Avoiding douching 48 hours before the test
- Avoiding medicinal or contraceptive vaginal creams 48 hours before the test
- Avoiding the use of tampons 48 hours before the test
Procedure Details
A Pap test is an outpatient procedure and does not need admission.
- Anaesthesia: No anaesthesia is required for a PAP test
- Duration: This test takes 2-3 min to perform.
The individual is asked to lie on their back on the examination table with their feet in foot stirrups and the tailbone at the table's edge. A metal or a plastic speculum is placed in the vagina to examine the cervix. A cervical broom or spatula is placed on the cervix and rotated in one direction to obtain the cells from the cervix. A cervical brush and a spatula may also be used to get the cells from the cervix. The specimen obtained is transferred to a liquid cytology vial or a glass slide labelled and sent to a laboratory for microscopic examination.
Post-procedure advice
The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis, and the individual can leave immediately after and resume their normal activities.
Interpretation of test results based on the presence of abnormal cells is done as follows:
- Low-grade intraepithelial lesions
- High-grade intraepithelial lesions
- Glandular cell abnormalities
The doctor will advise further treatment depending on the grade of abnormality.
Complications
There are rarely any complications associated with a PAP Smear test, and may include minor bleeding or infections.
Prognosis
A PAP smear is an effective screening and diagnostic tool that helps in the early detection of precancerous changes.
When combined with other confirmatory diagnostic tests such as colposcopy, it can help to increase significantly the early detection and management of precancerous stage and thereby prevents progression to cervical cancer.
When to contact the doctor or hospital?/ Indications for hospitalization if required
PAP Smear is done as an outpatient procedure, and no hospitalization is required. Medical attention is warranted in the rare event of heavy bleeding after the test.
Suggested clinical specialists/ Departments to consult for this procedure
- Gynaecology & obstetrics
Additional information
PAP Smear is advised to be done on a regular basis as follows:
- 21 years: Begin screening if sexually active
- 21-29 years: Once every 3 years
- 30-65 years: Every 5 years
- 65 years and above: Stop screening if previous negative history
- After hysterectomy: No screening is required if there is no history of precancerous conditions in the past 20 years
- HPV vaccinated women: To be screened similarly to those who are unvaccinated
Was this article helpful?
YesNo





10 Jul, 2023|10 months ago