Allergy
Blood Diseases
Bone & Joints
Brain
Cancer
Child Care
Cosmetic Surgery
Diabetes
Endocrinology
ENT
Eye
Gen Medicine
General Surgery
Heart
Kidney
Lifestyle
Liver & Digestive
Lung
Men’s Health
Mental health
Physiotherapy
Rheumatology
Skin and hair
Sleep Disorders
Spine
Transplant
Women Health
Thyroid
Vascular Surgery
Earwax Blockage
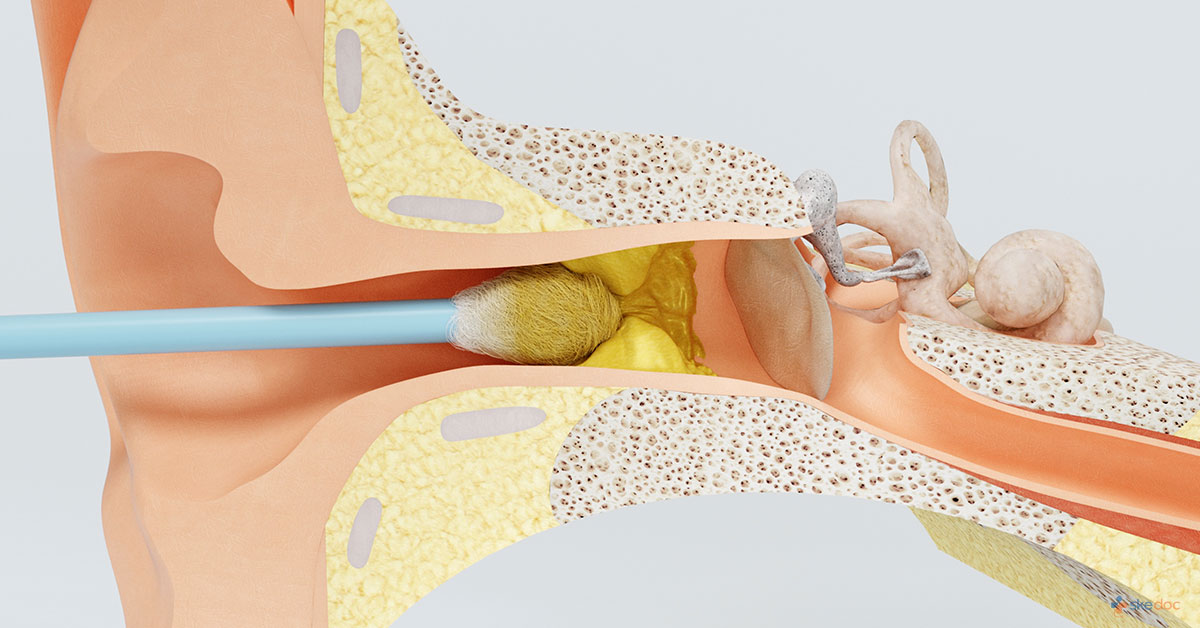
What Is Cerumen Impaction or Earwax Blockage?
Cerumen Impaction or Earwax Blockage is a condition when excess cerumen (earwax) accumulates in the ear canal and begins to cause symptoms, interferes with ear examination or both.
Alternate name
- Cerumen Impaction
Is this condition a medical emergency?
Earwax blockage is not a medical emergency.
Causes
Cerumen has an important role in trapping dust and foreign particles and preventing them from going deeper into the ear and causing harm. Cerumen provides lubrication which helps to prevent the scaling of the skin within the ear. It has antimicrobial properties and helps to prevent some infections. Old cerumen is naturally cleared by the body as new cerumen is produced and is aided by the movement of the jaw and epithelial migration in the ear canal. Under certain circumstances, the cerumen is either too hard to be naturally moved out or has been pushed too deep from where it cannot be removed naturally. This results in the impaction of cerumen or earwax blockage.
Some of the causes of earwax blockage are:
- Self attempts to clear earwax by using earbuds or other objects
- Excessive secretion of earwax
Symptoms & signs
Some of the symptoms and signs of earwax blockage may include:
- Ear pain
- A feeling of fullness in the ear
- Reduced hearing on the affected side
- Ringing in the ear
- Dizziness
- Cough
Investigations
No investigations are necessary to establish a diagnosis of earwax blockage other than a clinical evaluation via otoscopy.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of earwax blockage is established based on medical history and clinical evaluation.
Treatment options
The treatment of earwax blockage is the removal of the excess and accumulated cerumen from the ear canal using gentle intervention and medication.
A. Medical management
Medical management of earwax blockage includes:
- Cerumenolytics or Earwax softeners: Are used to soften the hard and impacted cerumen. Ideally used for 3-5 days before cerumen extraction
- Topical Anesthesia: Used before extraction of the cerumen
B. Interventional including surgery and indications for surgery
Impacted cerumen is removed by one of the following methods, preferably after it has been softened with earwax softeners.
- Curet: A specially shaped instrument is used to remove the impacted wax.
- Suction and irrigation: The softened and excess cerumen is sucked out using a special vacuum apparatus and the ear canal is irrigated (washed with lukewarm water).
There are certain conditions of earwax blockage under which the following is done:
- Irrigation is not done if there is a presence or a previous history of a perforated eardrum
- Suction is not done if the cerumen is very hard if there is severe ringing in the ears
- Suction is done with extreme care in Individuals who have previously undergone ear operations such as a mastoidectomy
C. Role of diet/exercise/lifestyle changes/preventive measures
It is not advisable to try and remove ear wax at home with kits that are available over the counter. It can lead to the cerumen being pushed deep inside and can result in serious complications such as rupture of the eardrum
Complications
Earwax blockage rarely causes complications. Complications can be seen however when attempts are made to remove the impacted earwax either by self or through unqualified personnel. Complications include:
- Rupture of the eardrum and Hearing loss
- Ear infections of the external ear
- Vertigo and dizziness
- Severe ringing in the ears
Prognosis
The prognosis for cerumen impaction is excellent if treated by a specialist after a thorough examination of the ear.
When to contact the doctor or hospital/How to identify the emergency or complications?
It is advisable to seek medical attention if the symptoms of earwax blockage persist over a few days and are affecting the ability to hear.
Indications for hospitalization if required
Hospitalization is not required for cerumen impaction.
Suggested clinical specialist/Departments to consult for this condition
Cerumen impaction will be attended to by specialists from the Department of Otorhinolaryngology (ENT).
Was this article helpful?
YesNo




