Allergy
Blood Diseases
Bone & Joints
Brain
Cancer
Child Care
Cosmetic Surgery
Diabetes
Endocrinology
ENT
Eye
Gen Medicine
General Surgery
Heart
Kidney
Lifestyle
Liver & Digestive
Lung
Men’s Health
Mental health
Physiotherapy
Rheumatology
Skin and hair
Sleep Disorders
Spine
Transplant
Women Health
Thyroid
Vascular Surgery
Leukoplakia
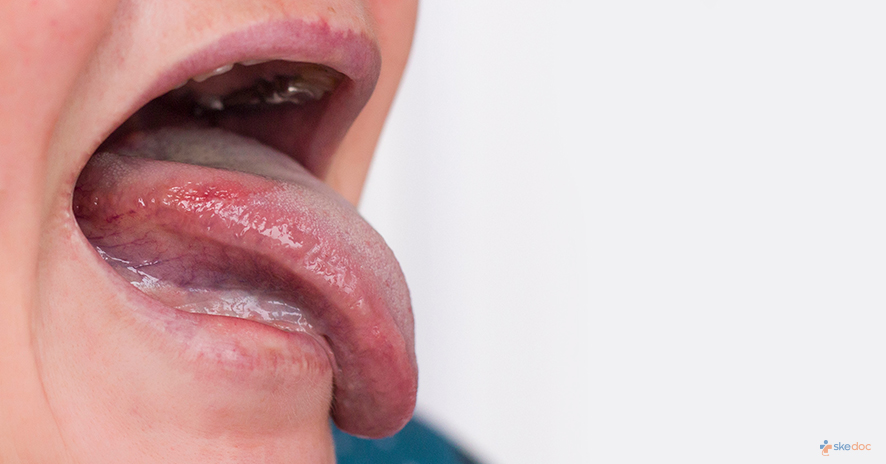
What is Leukoplakia?
Leukoplakia, also known as Oral Leukoplakia, is a precancerous condition that is seen inside the mouth and presents as a persistent white patch that cannot be rubbed off or removed. It is associated with tobacco smoking and chewing, and eating betel nuts. While it is most commonly seen in the mouth, it can also be present on the mucosal surfaces of the gastrointestinal tract and the genitals.
Is Leukoplakia condition a Medical emergency?
Leukoplakia is not a medical emergency.
Types
Leukoplakia may be of the following types:
- Homogenous Leukoplakia: The patch is uniform, white, thick and well defined
- Non-homogenous: The borders of the patch are not well defined, it may be a mix of red and white colour
- Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia: It is a high-risk type that is seen on the gums and the buccal (cheek) mucosa
- Erythroleukoplakia: It is seen as white nodular patches and has a higher risk of cancer
- Sublingual Leukoplakia: It is seen on the floor of the mouth
- Oral hairy Leukoplakia: It is white with a grooved surface and is usually caused by the Epstein Barr Virus (EBV)
Causes
The exact cause of Leukoplakia is not known. There is however a strong association between chewing or smoking tobacco and the consumption of betel nuts. Some factors that can cause Leukoplakia to include:
- Smoking or chewing tobacco
- Eating betel nuts
- Ragged sharp edges of the teeth causing irritation of the mucosal surface
- Ill-fitting dentures
- Long term alcohol use
- infection with Epstein Barr virus
Risk factors
Factors that increase the risk of Leukoplakia include:
- Gender: It is more common in men than in women
- Advanced age: It is more common in the 50-70 year age group
- Smoking or chewing tobacco
- Long term alcohol use
- Vitamin A and B deficiency
- Endocrine disturbances
- Candidiasis
Symptoms & signs
Leukoplakia does not cause any symptoms in a majority of cases. Symptoms if present includes:
- Pain
- Discomfort when opening the mouth wide
Investigations
There are no specific investigations that can be done to evaluate Leukoplakia and a physical examination and medical history are the mainstays of diagnosis. Some procedures that may be advised include:
- Oral brush biopsy: A small spinning brush is used to collect cells for histopathological analysis
- Excisional biopsy: A small part of the entire patch is removed for a histopathological diagnosis
Diagnosis
A diagnosis of Leukoplakia is established based on medical history, clinical evaluation, and results of the investigations done.
Treatment options
There are no proven treatments for the management of Leukoplakia other than the surgical removal of the entire patch. Some medications may be prescribed which help in a few cases of the condition.
Medical management
Medical management of Leukoplakia may include the following although none have a proven effect on curing the condition:
- Systemic retinoids
- Anti-inflammatory agents
- Caroteinoids
Interventional including surgery and indications for surgery
Surgical interventions for the management of Leukoplakia include complete removal of the patch. The following may be done:
- Surgical excision
- Cryotherapy
- Carbon dioxide laser ablation
Role of diet/ Exercise/ Lifestyle changes/ Preventive measures
Some measures that can be taken to prevent Leukoplakia include:
- Cessation of smoking or chewing tobacco
- Avoiding consumption of betel nuts
- Cessation of alcohol consumption
- Getting regular dental checkups
Complications
Some complications associated with Leukoplakia include:
- Increased risk of oral cancer
Prognosis
The prognosis for Leukoplakia is generally good, however, a sizable number of individuals with Leukoplakia tend to develop multiple oral cancers and poorer outcomes. Surgical removal of Leukoplakia does not guarantee a risk in the reduction of oral cancer.
When to contact the doctor or hospital? / How to identify the emergency or complications?
It is advisable to seek medical attention if painless white patches are noticed in the mouth, especially if there is a history of tobacco or alcohol use.
Indications for hospitalization if required
Brief hospitalization may be required for the surgical management of Leukoplakia.
Screening methods
Regular dental checkups are advised for individuals who smoke or chew tobacco and consume alcohol.
Suggested clinical specialist/ Department to consult for this condition
- Otorhinolaryngologist (ENT)
Was this article helpful?
YesNo




