Allergy
Blood Diseases
Bone & Joints
Brain
Cancer
Child Care
Cosmetic Surgery
Diabetes
Endocrinology
ENT
Eye
Gen Medicine
General Surgery
Heart
Kidney
Lifestyle
Liver & Digestive
Lung
Men’s Health
Mental health
Physiotherapy
Rheumatology
Skin and hair
Sleep Disorders
Spine
Transplant
Women Health
Thyroid
Vascular Surgery
Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
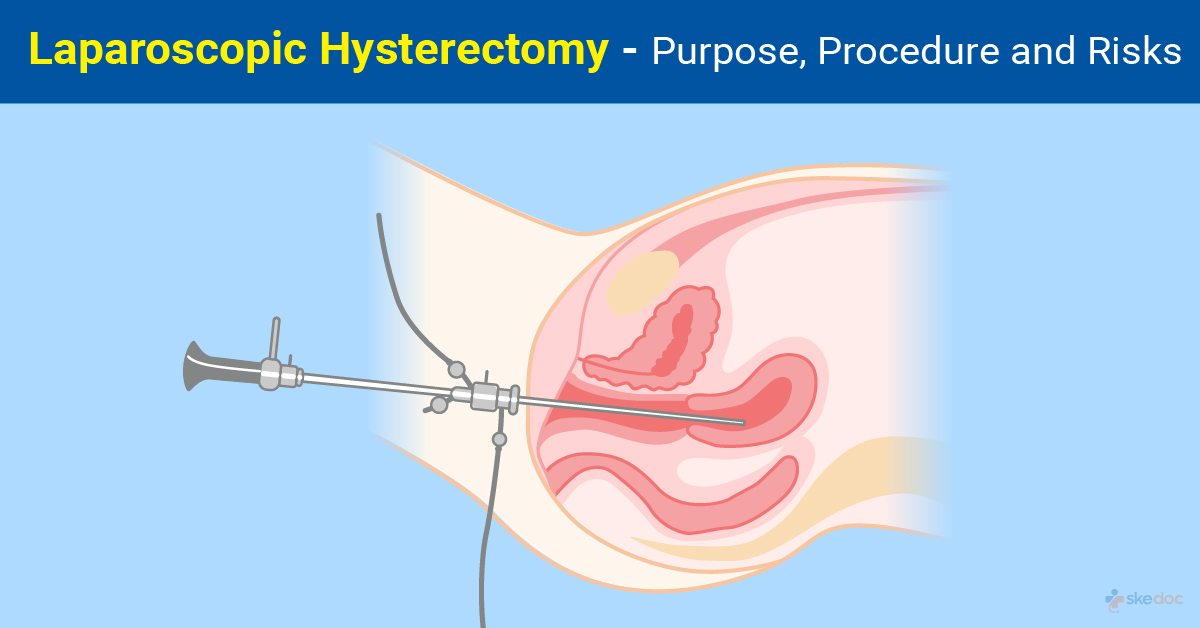
What is a Laparoscopic Hysterectomy?
Laparoscopic Hysterectomy, also known as Lap Hysterectomy, is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that is done to remove the uterus. It offers the advantages of shorter hospital stay, faster recovery, early resumption of activities, and lesser complications when compared to traditional and open surgical procedures for hysterectomy.
Is Laparoscopic Hysterectomy an elective or an emergency procedure?
Laparoscopic Hysterectomy is an elective procedure.
Types
Lap Hysterectomy may be of the following types:
- Diagnostic laparoscopy and vaginal hysterectomy
- Laparoscopic-assisted vaginal hysterectomy
- Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
- Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy (TLH Hysterectomy)
- Laparoscopic supracervical hysterectomy
- Vaginal hysterectomy with laparoscopic vault suspension
- Laparoscopic Hysterectomy with lymphadenectomy
- Laparoscopic Hysterectomy with lymphadenectomy and omentectomy
- Laparoscopic radical hysterectomy with lymphadenectomy
Indications
Some indications for Lap Hysterectomy include the following conditions:
- Endometriosis
- Adenomyosis
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Uterine fibroids
- Uterine Prolapse
- Uterine and gynecologic cancers
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Transgender: Male Affirmation
- Placenta Previa leading to severe bleeding after delivery
Contraindications and risk factors
Some contraindications for Lap Hysterectomy include the following:
- Inability to undergo general anesthesia
- Severe cardiopulmonary dysfunction
- Coagulopathies
- Severe adhesive pelvic disease: Seen in multiple cesarean sections, multiple laparotomies
- Obstructive fibroids
- Severe Obesity
Investigations before the procedure
Some investigations that may be done before Lap Hysterectomy include:
- Laboratory tests:
- CBP & ESR
- Coagulation profile and blood typing
- Liver and renal function tests
- Complete urine examination
- Blood Glucose/HbA1c
- Complete metabolic panel
- Serology testing
- Imaging tests:
- Abdominal and pelvic ultrasound
- CT/MRI
- Echocardiogram
- Electrocardiography (ECG)
- Pulmonary function tests
Preoperative advice
Before the surgery, the following are done:
- Risks and benefits of the procedure are explained
- Anticoagulant medications, if any, are stopped a few days before the surgery
- Antibiotic prophylaxis may be initiated a few days before the surgery
- Nothing by mouth after midnight on the night before surgery
Intraoperative details
- Duration: A lap hysterectomy may last between 1 and 3 hours, depending on the procedure that is being performed.
- Anesthesia: Laparoscopic Hysterectomy surgery is done under general anesthesia with intubation and epidural anesthesia for postoperative pain management.
Description of the procedure
With the individual lying on her back and the thighs slightly flexed, IV lines and the endotracheal tube are put in place, and after the general anesthetic has taken effect, a speculum is placed in the vagina, and the cervix is dilated. Multiple incisions are given in the abdomen, and the abdomen is insufflated. The laparoscope is introduced through the incision near the umbilicus, and the other surgical instruments are introduced through the remaining incisions.
The ligaments (round ligament and infundibulopelvic ligaments, and blood vessels (uterine vessels) attached to the uterus are coagulated, sectioned, and ligated. The uterus is then removed after freeing it from all its attachments in the pelvis. The uterus is removed through a small incision in the vagina if a vaginal hysterectomy is being done. If a laparoscopic supracervical hysterectomy is being done, a portion of the cervix is left behind. Depending on the procedure that is being done, the ovaries, the cervix, lymph nodes, and surrounding tissue may also be removed.
Care is taken to avoid injury to the urinary bladder and other important structures inside the pelvis. Abdominal insufflation is done, and the instruments are removed after confirming that there is no residual bleeding. The abdominal incisions are closed with absorbable sutures.
Postoperative details
After the surgery, the following are done:
- The individual is shifted to a recovery room and an ICU and monitored until awake and stable
- The cardiopulmonary function is monitored
- Extubation is done once the individual is stable
- Early ambulation is encouraged
- Liquids diet for the first 6 hours followed by a normal diet as tolerated
Common post-procedure occurrences are:
- Pain
- A feeling of fullness and abdominal bloating
- Lightheadedness and fatigue
- Slight vaginal bleeding
Discharge: Usually on the 2nd postoperative day if there are no complications.
Medications: Pain relievers and antibiotics may be prescribed.
Review: Usually 1 week after the procedure and regular check-ups thereon.
Resumption of normal activity: Usually 2- 3 weeks after the procedure.
Role of Diet/ Exercise/ Lifestyle changes
Some measures that are taken after a total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy surgery include:
- To bathe 48 hours after the procedure
- To avoid strenuous activity and lifting heavy weights for 2 weeks after the procedure
- Regular exercise can be resumed after 4 weeks
- Abstinence from sexual intercourse for 6 weeks
- Calcium supplementation for 3- 6 months
- Hematinic nutrition for 3 months
Complications
Some complications that may be seen with surgery include:
- Intraoperative and postoperative bleeding
- Infections
- Hernia at incision sites
- Injury to organs such as the bowel, bladder, ureters
- Bowel perforation
- Formation of pelvic adhesions
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Pulmonary embolism
- Cardiac complications due to anesthesia
Prognosis
The prognosis of the surgery is generally excellent, with faster recovery, shorter hospital stay, and less postoperative complications, although it also depends on the underlying condition that is being treated.
Indications for hospitalization if required
Brief hospitalization will be required.
Suggested clinical specialist/ Departments to consult for the procedure
It is done by specialists from the department of advanced laparoscopic gynecologic and obstetric surgery.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo
Comments





