Allergy
Blood Diseases
Bone & Joints
Brain
Cancer
Child Care
Cosmetic Surgery
Diabetes
Endocrinology
ENT
Eye
Gen Medicine
General Surgery
Heart
Kidney
Lifestyle
Liver & Digestive
Lung
Men’s Health
Mental health
Physiotherapy
Rheumatology
Skin and hair
Sleep Disorders
Spine
Transplant
Women Health
Thyroid
Vascular Surgery
Laparoscopic Colon Surgery
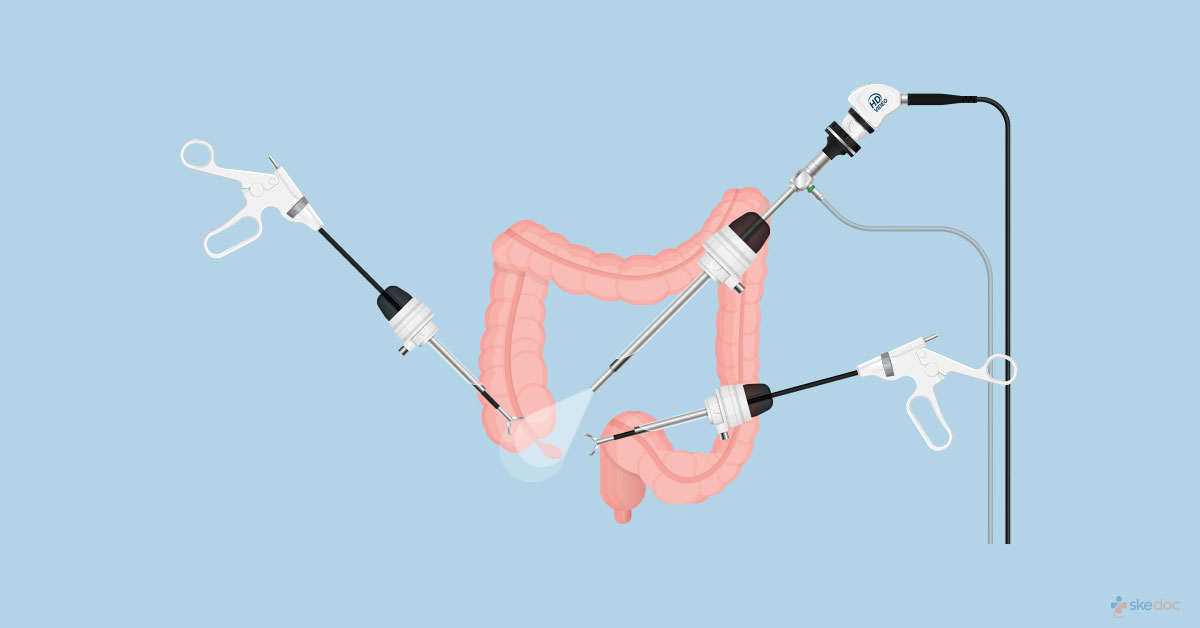
What Is Laparoscopic Colon Surgery?
Laparoscopic colon surgery is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that is done to treat diseases and conditions that affect the colon. It is done as an alternative to open surgery as it has fewer complications, shorter stay in the hospital, less postoperative pain, less scarring, and early return to normal activities.
Is this procedure an elective or an emergency procedure?
Laparoscopic colon surgery is done as an elective procedure.
Types of procedure
Laparoscopic colon surgery can be of the following types:
- Laparoscopic colectomy
- Laparoscopic total colectomy
- Laparoscopic partial colectomy
- Laparoscopic hemicolectomy
- Laparoscopic proctocolectomy
- Laparoscopic colostomy
Indications of laparoscopic colon surgery
The indications for Laparoscopic colon surgery may include the following:
- Bowel obstruction
- Bowel perforation
- Crohn's disease: When conservative treatment has failed.
- Colon Cancer or colorectal cancer
- Familial adenomatous polyposis
- High-risk precancerous colon polyps
- Ulcerative colitis
Contraindications and risk factors of laparoscopic colon surgeries
The contraindications for Laparoscopic colon surgery may include:
- Tumors infiltrating into adjacent structures
- Carcinomatosis
- Morbid obesity
- Multiple previous abdominal surgeries
- Extensive abdominal adhesions
- Tumor with resectable liver metastasis
Investigations before the procedure
Some investigations that may be done before Laparoscopic colon surgery may include:
- Lab tests-
- CBP and ESR
- Coagulation profile and blood typing
- Liver and renal function tests
- Blood glucose/HbA1c
- Complete urine examination
- Imaging tests-
- Chest x-ray
- Lower GI series of X-Rays
- MRI
- Procedures-
- Flexible Sigmoidoscopy
- Colonoscopy
- Barium Enema
Preoperative advice
Before Laparoscopic colon surgery, the following is done:
- Risks and benefits of the procedure explained
- Anticoagulant medication may be stopped a few days before surgery
- Antibiotic prophylaxis may be started a few days before surgery
- 5 days before low fiber diet, 3 days before a liquid diet is started, 2 days before clear liquids with milk of magnesia and nothing by mouth 8 hours before the procedure
- Colon cleansing and enema is done a few hours before the procedure
Intraoperative details
Duration: Laparoscopic colon surgery may last between 3 to 6 hours depending on the procedure that is being done.
Anesthesia: Laparoscopic colon surgery is usually done under general anesthesia with epidural anesthesia for postoperative pain management.
Description of the procedure:
With the individual lying on his/her back, IV lines and of a urinary catheter are put in place, and after the anesthesia has taken effect multiple small incisions are given in the abdomen. A fiber-optic scope this passed through one of the incisions and other surgical instruments are passed through the other incisions after insufflation of the abdomen is done. Depending on the underlying condition part or whole of the colon may be cut and removed, polyps and growths may be removed, narrowing or strictures of the colon may be dilated. Further, depending on the procedure that was done, the cut ends of the colon may be reattached, the ileum may be attached to the anal canal (ileoanal anastomosis), an opening might be made in the abdomen called an ostomy to which either the colon (colostomy) or the ileum (ileostomy) may be attached to remove the waste from the body through a pouch (colostomy bag) which is attached to the opening. In some cases, laparoscopic surgery may need to be converted into open surgery.
Laparoscopic right colectomy or right hemicolectomy: In a laparoscopic right hemicolectomy the terminal portion of the ileum (small intestine), the right colon, or the ascending colon, the beginning of the transverse colon are removed. This is followed by an anastomosis (joining) of the ileum with the remaining portion of the transverse colon. If a right hemicolectomy is being done for a cancerous lesion in the colon then the amount of colon removed depends on the spread of cancer.
Laparoscopic left colectomy or left hemicolectomy: In a laparoscopic left hemicolectomy the rectum, the sigmoid colon, and the distal portion of the transverse colon are removed and a coloanal anastomosis is done in which the remaining part of the transverse colon is joined with the anal canal.
Laparoscopic total or subtotal colectomy: In a laparoscopic total or subtotal colectomy, the entire colon is removed, and usually, the lower portion of the rectum is left behind. The small intestine is joined with the rectal canal to create an ileorectal anastomosis.
Laparoscopic colostomy: In a laparoscopic colostomy, the remaining functional bowel is brought to the opening (stoma) created in the abdominal wall to enable fecal diversion. The feces from the bowel is collected via the stoma in the abdominal wall into a colostomy bag. A colostomy may be a temporary procedure or a permanent procedure. A temporary colostomy is also known as a loop colostomy and this procedure can be reversed at a later date. A permanent colostomy is also called an end colostomy. A colostomy may be a transverse colostomy in which the transverse colon is brought out through the stoma which is usually present on the upper part of the abdomen, or an ascending colostomy in which the ascending or right colon is brought out through the stoma which is present on the right side of the abdomen, or a descending colostomy in which the descending colon or the left colon is brought out through the stoma which is present on the left side of the abdomen.
Postoperative details
After Laparoscopic colon surgery, the following is usually done:
- The individual is shifted to a recovery room and monitored until awake and stable.
- Cardiopulmonary functions are monitored.
- Feeding is done via a nasogastric tube.
- The individual is encouraged to ambulate on the evening of the surgery.
- Extubation is done once bowel function returns.
Common post-procedure occurrences after laparoscopic colorectal surgery are:
- Pain at the site of surgery
- Nausea and vomiting
- Lightheadedness
- Passage of bloody mucus and gas into the colostomy bag for the first few days after the procedure.
Discharge: Usually 3 to 4 days after the procedure.
Medication: Pain relievers and antibiotics are generally prescribed.
Review: Usually one day 5-7 after the procedure.
Resumption of normal activities: Usually with some restrictions 10- 15 days after the procedure.
Role of diet/exercise/lifestyle changes
Some measures that may be taken after Laparoscopic colon surgery include:
- Avoiding strenuous activities for 1 to 2 weeks after the surgery
- Following the diet as advised by the physician
- Watching out for any signs of complications
Complications of laparoscopic colon surgery
Some complications that are associated with Laparoscopic colon surgery may include:
- Hemorrhage
- Bowel obstruction
- Wound infection
- Anastomotic leakage
- Urinary tract infection
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pneumonia
- Trocar site hernia
- Ureteral stenosis
- Psychological complications such as embarrassment, depression, etc.
Prognosis
The prognosis for Laparoscopic colon surgery generally depends on the underlying condition that is being treated as well as on the general health of the individual. The morbidity and mortality associated with Laparoscopic colon surgery are generally less when compared to open surgery.
Indications for hospitalization if required
Hospitalization will be required for Laparoscopic colon surgery or colorectal cancer surgery.
Suggested clinical specialist/Departments to consult for the procedure
Laparoscopic colon surgery will be done by specialists from the Department of Interventional Endoscopic Surgery and Functional Bowel Gastroenterology.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo




