Allergy
Blood Diseases
Bone & Joints
Brain
Cancer
Child Care
Cosmetic Surgery
Diabetes
Endocrinology
ENT
Eye
Gen Medicine
General Surgery
Heart
Kidney
Lifestyle
Liver & Digestive
Lung
Men’s Health
Mental health
Physiotherapy
Rheumatology
Skin and hair
Sleep Disorders
Spine
Transplant
Women Health
Thyroid
Vascular Surgery
Laminectomy
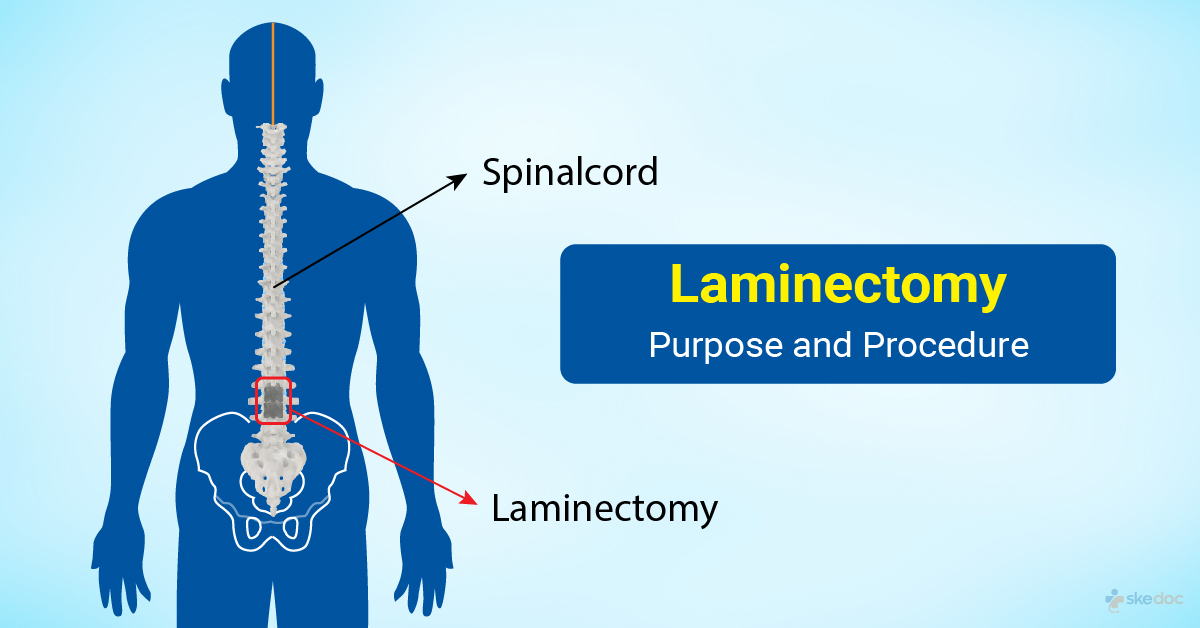
What is Laminectomy?
Laminectomy, also known as Decompression Surgery, is a surgical procedure performed to remove a portion or all of the vertebral bone called the lamina.
Is the laminectomy procedure an elective or an emergency procedure?
Laminectomy is an elective procedure.
Types
Laminectomy can be performed in any portion of the spine. Depending on the location of the surgery, it is classified as the following:
- Cervical Laminectomy: This refers to the removal of the lamina in the neck area
- Lumbar Laminectomy: It refers to the removal of the lamina in the lower back area
- Sacral Laminectomy: It refers to the removal of the lamina in the back between the pelvic and hip bones
- Thoracic Laminectomy: This refers to the removal of the lamina in the middle part of the back
Indications
The primary reason for performing a laminectomy surgery is to relieve pressure on the spinal cord and nerves that are caused due to abnormal growth of bones within the spinal canal. The abnormal bony outgrowths compress the spinal canal resulting in various complications. However, decompressive laminectomy does not cure any spine problems nor can it prevent permanent nerve damage caused by long-term spinal cord compression.
Laminectomy surgery is recommended in the following cases:
- In the treatment of severe spinal stenosis
- In the treatment of bone spurs, herniated discs, spondylosis, degenerative disc disease, and sciatica
- To remove or reshape the spinal discs
- To create space for removing a spinal tumor
- In the treatment of spinal deformity causing muscle weakness or numbness, making it difficult to stand or walk
- In the treatment of spinal deformity causing loss of bladder or bowel control
- In the treatment of spinal deformity that has failed conservative treatments like medications and physical therapy
Laminectomy surgery is also performed in association with spinal surgeries such as herniated disc surgery and spinal fusion.
Contraindications and Risk factors
Absolute contraindications for not performing a Laminectomy surgery are spinal instability. Other relative contraindications include degenerative or isthmic spondylolisthesis, severe scoliosis, and severe kyphosis.
Investigations before the procedure
Investigations that are done before performing a decompressive laminectomy surgery are imaging tests like MRI and CT scans to identify the spinal deformity and to determine the severity of the condition.
Preoperative advice
Before performing a decompressive laminectomy surgery:
- Risks and benefits of the surgery are discussed
- Eating and drinking after midnight the night before the surgery is discontinued
- Smoking before the procedure is discontinued to improve the healing process after the surgery
- Certain medications like aspirin, ibuprofen, and blood thinners are discontinued before the surgery
Intraoperative details
Anaesthesia: A laminectomy surgery is performed under general anaesthesia.
Description of procedure
Throughout the surgery, heart rate, blood pressure, and blood oxygen levels are monitored. The surgical area on the back is cleaned with an antiseptic solution. After administration of general anaesthesia, an incision is made on the back over the affected vertebrae. The size of the incision depends upon the medical condition for performing the decompressive laminectomy surgery. The incision is gently carried down to move the muscles apart from the spine.
Small surgical instruments are used to remove the bony arch of the vertebra called the lamina. An appropriate portion of the lamina is removed. Any abnormal bony spurs or growths are also removed. Spinal surgeries like disc herniation surgery, spinal fusion, or spinal tumor removal are also performed during laminectomy if required. At the end of the surgery, the incision is closed with stitches and a sterile bandage is applied over the incision site.
Laminectomy surgery may be performed via two approaches:
- MicroLaminectomy: This is a minimally invasive approach. Small incisions are made on the back. An arthroscope is inserted through one of the incisions. An arthroscope is an instrument with a tiny video camera on its tip, which displays the magnified view of the spinal structures on the monitor. Surgical instruments are inserted through other incisions for performing a decompressive laminectomy. This type of approach results in a smaller incision, less pain, and faster recovery. It causes less damage to tissues and surrounding organs.
- Open surgery: This type of approach requires a large incision in the back over the affected vertebra. The length of the incision depends on how many vertebrae are affected and need treatment. The open approach allows direct visualization and access to the surgical area. It involves more cutting and displacement of muscle and other tissues. However, the open surgery approach is a safe and more effective method in certain cases.
Postoperative details
Postoperatively after a decompressive laminectomy surgery:
- Take pain medications as prescribed for pain and discomfort.
- Keep the surgical incision area clean and dry.
- Observe the incision site for any signs of infection such as an increase in pain, fever, redness, swelling, bleeding, or drainage.
- Physical therapy is recommended to improve strength and flexibility.
- Follow-up as scheduled by the physician for removal of staples or stitches.
Role of Diet/ Exercise/ Lifestyle changes
Aftercare instructions for a decompressive laminectomy surgery are:
- Avoid walking, sitting, and standing for long hours
- Practice good posture
- Perform exercises to strengthen the back and leg muscles
- Avoid strenuous physical activities
- Avoid heavy lifting
- Avoid driving until recommended by the physician
- Avoid bending over to pick up objects
- The recovery period after a Laminectomy depends on the operative approach used and the medical condition of the individual
Complications
Complications that arise from a laminectomy surgery are:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Spinal nerve injury
- Blood vessel damage
- Spinal fluid leak
- Adverse reaction to anaesthesia
- No pain relief or little relief from pain
- Chance of recurrent symptoms
Prognosis
The overall prognosis of decompression surgery varies from individual to individual. In 80% of the cases, decompression surgery decreases pain and improves symptoms caused by spinal deformities. In some cases, there may not be considerable pain relief after the surgery. The success rate of the surgery depends on the specific reason for the operation.
Indications for hospitalization if required
If the surgery performed is just Laminectomy, it can be done on an outpatient basis and the individual can be discharged on the same day of surgery. If the procedure is associated with any spinal surgery, hospitalization is required.
Suggested clinical specialist/ Department to consult for the procedure
- Orthopedic surgeon
Was this article helpful?
YesNo




