Allergy
Blood Diseases
Bone & Joints
Brain
Cancer
Child Care
Cosmetic Surgery
Diabetes
Endocrinology
ENT
Eye
Gen Medicine
General Surgery
Heart
Kidney
Lifestyle
Liver & Digestive
Lung
Men’s Health
Mental health
Physiotherapy
Rheumatology
Skin and hair
Sleep Disorders
Spine
Transplant
Women Health
Thyroid
Vascular Surgery
Ingrowing Toenail
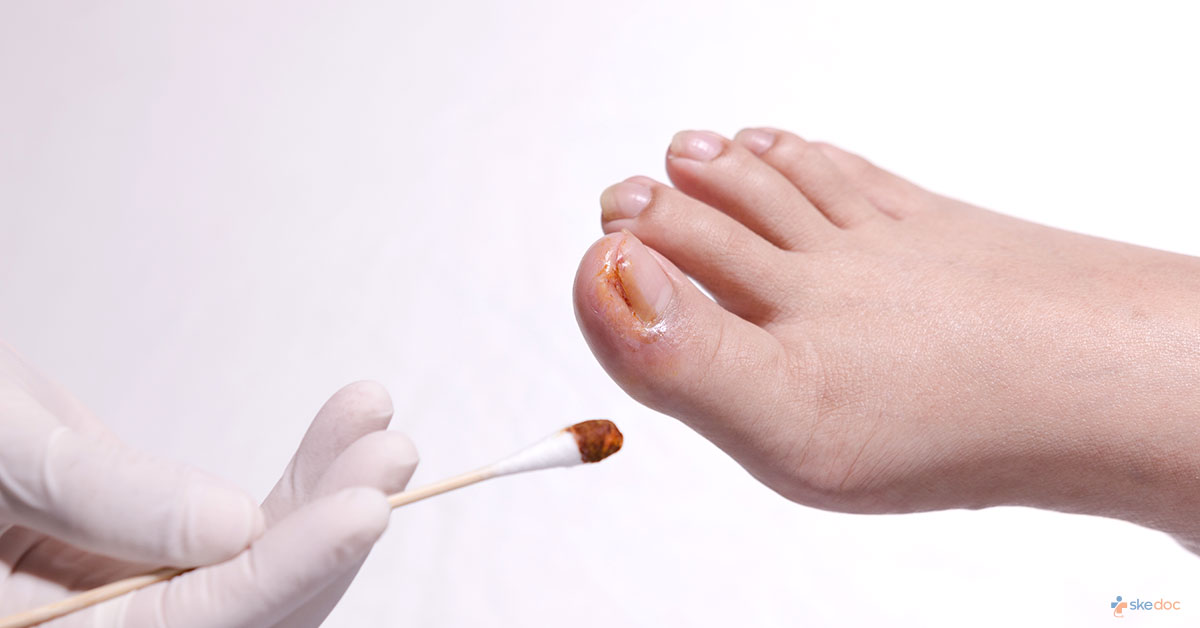
What is Ingrowing Toenail?
An Ingrowing Toenail, also known as unguis incarnatus, is a condition in which the nail grows into the skin next to the nail. The big toe is most likely to get affected.
Is Ingrowing Toenail a Medical emergency?
An Ingrowing Toenail is not a medical emergency.
Causes
Causes of an Ingrowing Toenail include:
- Irregular or curved toenails
- Cutting toenails incorrectly
- Wearing tight footwear that places a lot of pressure on big toes. Even tight socks or stockings can put pressure on the toes
- Injury to the toenail either by stubbing the toe, dropping a heavy object on the toe, or kicking a ball repeatedly
- Poor foot hygiene, such as not keeping the feet clean and dry
- Using feet extensively during sports, such as ballet, football, kickboxing, soccer, which includes repeated kicking or putting pressure on the feet. Any kind of pressure on the feet can cause damage to the toenails resulting in Ingrowing Toenails.
Risk factors
Ingrowing Toenail mainly occurs in people having sweaty feet. Teenagers mostly have sweaty feet. Therefore, the condition is more common in teenagers. Also, individuals having thick toenails are at an increased risk of developing Ingrowing Toenails.
Symptoms & signs
Signs and symptoms of Ingrowing Toenails are as described below:
- The skin next to the nail gets red, tender, or swollen
- Pain with pressure on the toe
- Fluid accumulation around the toe. In severe cases, it can ooze pus
- Bleeding
- Overgrowth of skin around the toe
- If the ingrown toe is not treated promptly it may lead to worsening symptoms
Investigations/ Diagnosis
Ingrowing Toenails are diagnosed on physical examination. If the toe is infected additional tests include an x-ray to show how deep the nail has grown under the skin. The x-ray also reveals if the ingrown nail was caused by the injury.
Treatment options
Medical treatment
Early stages of Ingrowing Toenails are treated at home. If there are any signs of infection, medical treatment is required. Signs of infection include redness, swelling, pain, warmth, and pus drainage. Medical treatment for Ingrowing Toenails includes:
- Acetaminophen for pain
- Topical antibiotics such as polymyxin, and neomycin to prevent infection
Interventional treatment including surgery and indications for surgery/ Surgical treatment
If there are signs of infection surgery is recommended. Surgical treatment for Ingrowing Toenail includes:
- Partial nail removal: Only a part of the nail is removed by digging into the skin under local anaesthesia. This procedure is successful in 99% of the cases and it is effective in preventing future Ingrowing Toenails. The sides of the nail are cut away, making the edges completely straight. A piece of cotton is placed under the remaining portion of the nail to keep the Ingrowing Toenail from recurring. A compound called phenol is used to keep the nail from growing back.
- Complete nail removal: In this procedure, the whole nail is removed. This is recommended when the ingrown nail is caused by thickening. Under local anaesthesia, the entire nail is removed. This procedure is called matrixectomy. After the surgery, the toe is covered with bandages. The foot should be kept elevated for one to two days. Special footwear is recommended to help the toe to heal properly. Avoid movement of the foot as much as possible. Saltwater soaks are done until the toe heals. Pain medications are prescribed for pain and discomfort. Antibiotics are given to prevent an infection after surgery.
If the nail is removed only partially, the nail can grow back in a few months. If the entire nail is removed from the base, the nail takes over a year to grow back.
Role of diet/ Exercise/ Lifestyle changes/ Preventive measures
Ingrowing Toenails can be treated at home by following some of the below instructions:
- Soak the feet in warm soapy water for 15 to 20 minutes three to four times a day. Also, soak the feet in apple cider vinegar
- After each soaking, put fresh bits of cotton or waxed dental floss under the ingrown edge
- Apply topical antibiotic cream
- Take pain medications for pain and discomfort
- While going outdoors, wear socks, stockings or footwear that does not put pressure on the toes
- Wear toe protectors that fit around the affected area. Toe protectors come as rings and can cover the entire toe
- Wear toe braces to protect the toe. They help to shield the skin from a sharp, ingrown nail and lift the nail edges as the nail grows
Ingrowing Toenails can be prevented by following certain tips:
- Trim toenails straight across
- Avoid cutting the edges
- Avoid cutting toenails too short
- Wear proper-fitting shoes, socks, or stockings
- If toenails are curved or thick by nature, surgery is required to prevent Ingrowing Toenails
Complications
Complications arise only if the toe is left untreated for a prolonged period. Complications are as described below:
- If left untreated, the infection can spread to the bone beneath the nail. It can also cause foot ulcers or open sores
- The toe would have decreased blood flow to the infected area
- Infection can cause tissue decay and tissue death
- The infection gets severe if diabetes is present
- A small cut or scrape of the Ingrowing Toenail can cause infection due to a lack of blood flow
Prognosis
Ingrowing Toenails can be treated at home; however, if they are persistent they require medical treatment. Complications increase if the individual has diabetes or other conditions that cause poor blood circulation. If the Ingrowing Toenail is causing persistent pain, infection, other painful foot issues requiring multiple treatments then surgical treatment is recommended to remove the partial or entire nail from the base. The overall prognosis of Ingrowing Toenails is good.
When to contact the doctor/ How to identify the complications?
Medical consultation is recommended under the following conditions:
- Failure of home treatment
- Persistent or worsening symptoms
- Difficulty walking
- Inability to perform activities
- Signs of infection
Indications for hospitalization
Ingrowing Toenails do not require hospitalization. Treatment is provided on an outpatient basis.
Suggested clinical specialists/ Department to consult for this condition
- General surgery
Was this article helpful?
YesNo




