Allergy
Blood Diseases
Bone & Joints
Brain
Cancer
Child Care
Cosmetic Surgery
Diabetes
Endocrinology
ENT
Eye
Gen Medicine
General Surgery
Heart
Kidney
Lifestyle
Liver & Digestive
Lung
Men’s Health
Mental health
Physiotherapy
Rheumatology
Skin and hair
Sleep Disorders
Spine
Transplant
Women Health
Thyroid
Vascular Surgery
Heart Enlargement
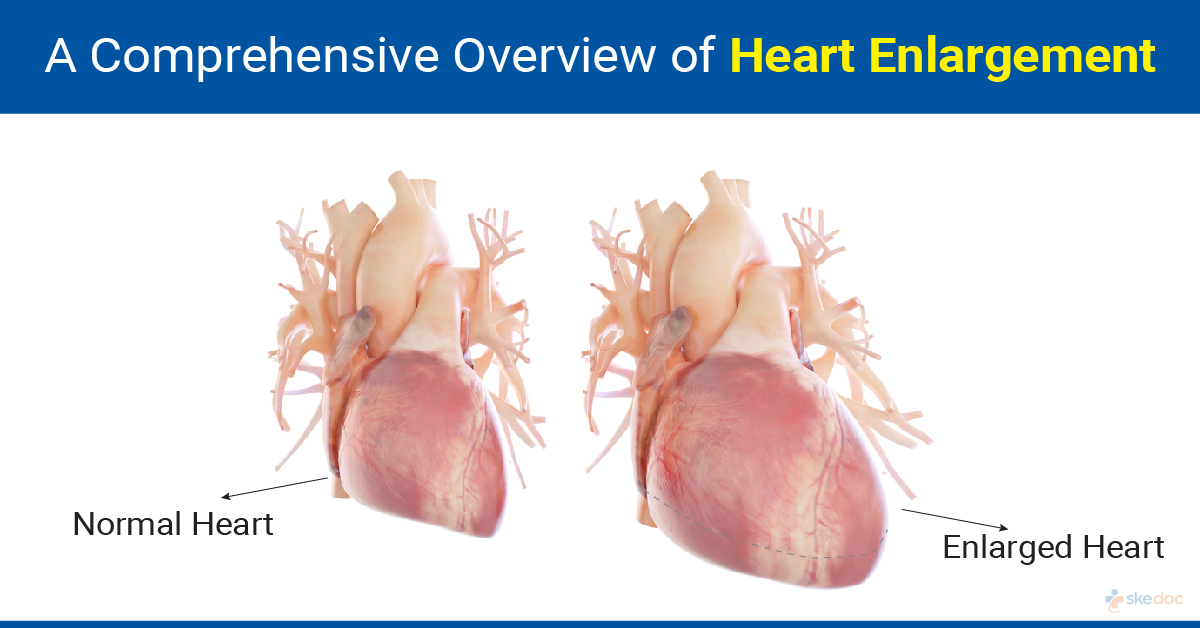
What is Heart Enlargement?
Heart enlargement is a condition in which the size of the heart is increased. An enlarged heart cannot pump blood efficiently and eventually leads to heart failure. It is not a disease in itself but is something that develops as an initial compensatory mechanism of the heart in response to other diseases or conditions affecting normal heart function.
Alternate names
- Enlarged Heart
- Cardiomegaly
- Megacardia
- Megalocardia
Is this condition a medical emergency?
Cardiomegaly is not a medical emergency, but early medical attention is warranted to prevent potentially fatal complications.
Types of this condition
Cardiomegaly may be of the following types
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy: The walls of the left or the right ventricles become stretched and thin.
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: The muscles of the ventricles become very thick.
Based on the structure of the heart involved
- Ventricular hypertrophy: The lower chambers are enlarged.
- Atrial Hypertrophy: The upper chambers are enlarged.
A condition called Athletic heart syndrome is seen in athletes and is a non-pathological condition in which the heart is enlarged and the resting heart rate is very low.
Causes of heart enlargement
The exact cause of cardiomegaly is not fully understood, but a few factors contribute to its development over time, and they include
- High blood pressure
- Coronary Artery Disease
- Heart Valve Disease
- Pulmonary Hypertension
- Thyroid Disorders
- Viral Infections of the heart
- Pregnancy: usually seen close to the time of delivery
- Anemia
- End-stage renal disease
- Diabetes
- Hemochromatosis
- Amyloidosis
- Chagas Disease
- HIV/AIDS
- Alcoholism
- Cocaine abuse
Risk factors
Some risk factors for heart enlargement may include
- Smoking
- High Cholesterol
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Family history of cardiomegaly
- Sleep apnea
- Sustained cardiac arrhythmias
- Congenital heart disease
Symptoms & signs of heart enlargement
Some of the symptoms and signs associated with this condition depend on the type of heart enlargement and may include the following
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy:
- Fatigue
- Dyspnea on exertion
- Shortness of breath
- Cough
- Orthopnea: Breathlessness at rest
- Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea: Breathlessness at night when asleep
- Increasing weight or abdominal width and fluid retention
- Fast respiratory rate
- Fast heart rate
- Low or high blood pressure
- In advanced or severe cases, the following may be seen
- Pulmonary edema
- Enlarged liver
- Ascites
- Prominent neck veins
- HCM can include the following:
- Dyspnea, shortness of breath on exertion
- Dizziness
- Fainting spells, Syncope, and presyncope
- Chest pain
- Palpitations
- Orthopnea
- Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
- Signs of congestive heart failure
- Neck veins are prominent
- Ventricular Hypertrophy: Mostly asymptomatic, symptoms are seen when the condition is severe enough to cause heart failure
- Chest Pain
- Breathlessness
- Palpitations
- Abnormal heart rhythms
- Dizziness
- Fainting or Syncope
- Rapid heart rate
- Elevated blood pressure
- Prominent neck veins
- Rapid respiratory rate and decreased breath sounds
Investigations
Some investigations that may be done for heart enlargement include
- Laboratory tests:
- CBP & ESR
- Liver and Renal Function tests
- Coagulation profile
- Complete Metabolic Panel
- Complete urine examination
- Viral Serology tests
- Serum Transferrin levels
- Blood Glucose/HbA1C
- Imaging tests:
- Chest X-Ray
- Echocardiography
- CT scan
- Cardiac MRI
- Angiography
- Electrocardiography (ECG)
- Cardiac Catheterization
- Stress Tests
- Pulmonary Function Tests
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on medical history, clinical evaluation, and results of the investigations done.
Treatment options
The treatment depends on the type of enlargement and the underlying cause. Medical management or surgical intervention may be required.
Medical management
Medical management of heart enlargement depends on the underlying cause and may include
- Diuretics: To lower the workload on the heart
- ACE inhibitors: To lower the blood pressure and the workload on the heart
- Angiotensin II Receptor blockers: To lower the blood pressure and the workload on the heart; used in individuals who cannot be given ACE inhibitors.
- Beta-Blockers: To lower blood pressure and improve heart muscle contraction
- Anticoagulants: To lower the risk of blood clot formation
- Antiarrhythmic Agents: To suppress heart rhythm disorders
Interventional including surgery and indications for surgery
Interventions for the management of heart enlargement depend on the underlying cause and may include
- Implantable devices
- Pacemakers: For dilated cardiomyopathy.
- Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator: When serious heart rhythm disorders are present in addition to heart enlargement.
- Heart Valve Surgery: This may be required if heart valve disease is the cause of heart enlargement.
- Coronary Bypass Surgery: May be required if coronary artery disease is responsible for heart enlargement.
- LVAD: A left ventricular assist device may be required if the heart is in an advanced stage of failure and can no longer be managed with medication.
- Heart Transplant: If the heart enlargement has reached a stage of failure that cannot be managed conservatively or with other surgical interventions.
Role of Diet/Exercise/Lifestyle changes/ Preventive measures
Some measures that can be taken to reduce the risks of heart enlargement include
- Keep hypertension under control
- Keep diabetes under control
- Cessation of smoking
- Exercise, eat a healthy diet, and maintain ideal body weight
- Avoid stress
- Avoid recreational drug use
- Get periodic medical and cardiologic consultations if suffering from heart valve or other cardiac diseases or if there is a family history of heart enlargement.
Complications of heart enlargement
Some of the complications that may be seen with heart enlargement include
- Pulmonary thromboembolism
- Heart Failure
- Stroke
- Myocardial Infarction
- Cardiac Arrest
- Sudden death
Prognosis
The prognosis of heart enlargement depends on the underlying cause. The presence of coronary artery disease or other comorbidities increases the likelihood of a poor prognosis if not detected early and managed properly.
When to contact the doctor or hospital? / How to identify the emergency or complications?
It is advisable to seek medical attention if the symptoms and signs of heart enlargement are noticed.
Indications for hospitalization if required
Hospitalization will be needed if surgical management is required.
Screening methods for an enlarged heart
Individuals with a family history of heart enlargement should get periodical cardiologic check-ups done.
Suggested clinical specialist/Departments to consult for enlarged heart
Cardiomegaly will be attended to by specialists from the Department of Cardiology, Heart Failure & Transplant Cardiology.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo




