Allergy
Blood Diseases
Bone & Joints
Brain
Cancer
Child Care
Cosmetic Surgery
Diabetes
Endocrinology
ENT
Eye
Gen Medicine
General Surgery
Heart
Kidney
Lifestyle
Liver & Digestive
Lung
Men’s Health
Mental health
Physiotherapy
Rheumatology
Skin and hair
Sleep Disorders
Spine
Transplant
Women Health
Thyroid
Vascular Surgery
Haemorrhoidectomy
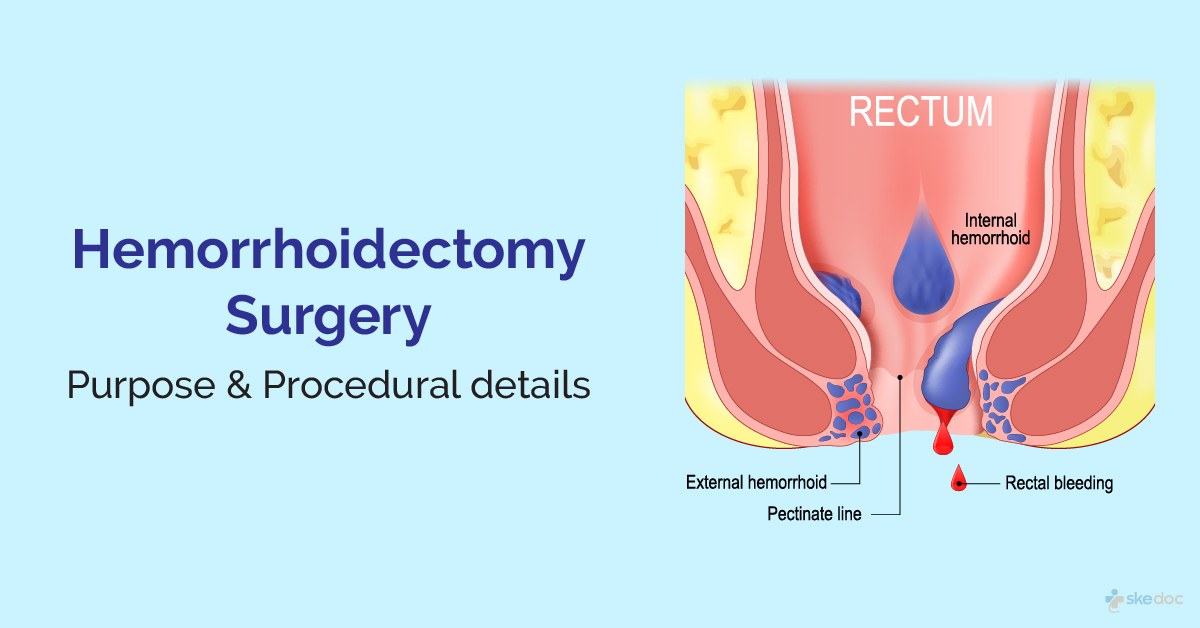
What is Hemorrhoidectomy?
Hemorrhoidectomy is a surgical procedure to treat and manage hemorrhoids or piles. Hemorrhoids are inflamed and swollen vascular structures in the anal canal often associated with increased intra-abdominal pressure, as seen with straining during defecation, irregular bowel habits, etc.
Is Hemorrhoidectomy an elective or an emergency procedure?
Hemorrhoidectomy is usually done as an elective procedure and may sometimes be done as an emergency.
Types
Hemorrhoidectomy may be of the following types
- Excisional Hemorrhoidectomy
- Open excisional Hemorrhoidectomy
- Closed excisional Hemorrhoidectomy
- Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy or Circumferential mucosectomy or PPH
Indications
It is indicated for the management of hemorrhoids in the following circumstances:
- Thrombosed external hemorrhoids
- Failure of conservative or nonsurgical treatment of hemorrhoids
- Grade 3 and grade 4 hemorrhoids with very severe symptoms
- When hemorrhoids are present along with anal fistula or anal fissure
- When hemorrhoids with skin tags cause hygiene issues
- Haemorrhoids with a history of multiple thromboses
- Patient preference
- Primarily complaining of bleeding
Contraindications and Risk Factors
Hemorrhoidectomy is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- Fecal incontinence
- Rectocele
- Bleeding disorders
- Portal hypertension with rectal varices
- Crohn's Disease
This condition can be handled and treated by giving a pudendal nerve block and performing a laser or chivate procedure.
Investigations before the procedure
Some investigations that may be done before hemorrhoidectomy include:
- Laboratory tests:
- CBP and ESR
- Coagulation profile and blood typing
- Liver and renal function tests
- Blood glucose/HbA1c
- Procedures:
- Anoscopy
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy
Preoperative advice
Before hemorrhoidectomy, the following is done:
- The risks and benefits of the procedure are explained
- Anticoagulant medication may be stopped before the surgery
- Nothing by mouth after midnight on the night before surgery
- Colon cleansing or saline enema is done before the procedure
Intraoperative details
- Duration: Hemorrhoidectomy may last between 30 to 45 minutes.
- Anesthesia: Hemorrhoidectomy is done under bilateral pudendal nerve block with local anesthesia; general anesthesia may be used in rare cases.
Description of the procedure
Excisional Hemorrhoidectomy
The individual is placed in a jackknife position, a bilateral pudendal nerve block is done, and a local anesthetic with epinephrine is injected into the area after the buttocks are retracted to expose the anus. A retractor is placed in the anal canal, and the prolapsed hemorrhoid is grasped, sutured first (to minimize blood loss), and then resected with scissors or electrocautery. The wound is then closed with an absorbable suture, and packing is done and covered with gauze. The difference between a closed and an open hemorrhoid is that the anal mucosa is sutured in a closed haemorrhoid. In contrast, in an open hemorrhoid the anal mucosa is left open and not sutured. Using electrocautery or ultrasound energy devices to remove the hemorrhoids is associated with lesser postoperative complications than conventional excision with other surgical instruments.
Stapled Hemorrhoidectomy
The individual is placed in a jackknife or lithotomy position, a bilateral pudendal nerve block is done, and a local anesthetic with epinephrine is injected into the area after the buttocks are retracted to expose the anus (general anesthesia lesion may be used sometimes). A retractor is placed in the anal canal, a pursestring suture is applied in the mucosal layer, and a stapler is introduced. The prolapsed hemorrhoid is dissected entirely along with a ring of mucosa and submucosa within the canal, after which the distal mucosa is stapled over the proximal mucosa. The wound is closed with an absorbable suture, and packing is done and covered with gauze.
Postoperative details
After the surgery, discharge is usually done on the same day after briefly monitoring for immediate postoperative complications.
- Common post-procedure occurrences: Pain is usually present for 1 to 2 weeks.
- Medications: Pain relievers and antibiotics are generally prescribed.
- Review: This will usually be 4 to 6 weeks after the procedure.
- Resumption of normal activities: With some restrictions on the second or third postoperative day.
Role of Diet/ Exercise/ Lifestyle changes
Some measures that need to be taken after a Hemorrhoidectomy include:
- Packing is removed after 24 hours, and the outer gauze is changed daily as required
- Eat a high-fibre diet
- Use stool softeners, bulking agents
- Avoid straining during defecation, coughing, sneezing, and lifting heavy weights for a week or two after the procedure
Complications
Some complications that can be seen after Hemorrhoidectomy include:
- Pain
- Bleeding
- Infections
- Urinary retention
- Anal stenosis [narrowing of the anal canal]
- Poor wound healing
- Abscess of fistula formation - Usually results from poor wound healing
- Incontinence - usually resolves within 6-8 weeks
Stapled Hemorrhoidectomy is associated with lesser postoperative pain, shorter recovery time, and lesser complications than conventional surgery to remove hemorrhoids.
Prognosis
The prognosis for Hemorrhoidectomy is generally good, although there is a risk of recurrence after the procedure. Recurrence is more commonly seen with conventional surgery to remove hemorrhoids.
Indications for hospitalization if required
Hospitalization is usually not required for Hemorrhoidectomy.
Suggested clinical specialist/ Department to consult for the procedure
Specialists from the Department of General Surgery do hemorrhoidectomy.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo
Comments





