Allergy
Blood Diseases
Bone & Joints
Brain
Cancer
Child Care
Cosmetic Surgery
Diabetes
Endocrinology
ENT
Eye
Gen Medicine
General Surgery
Heart
Kidney
Lifestyle
Liver & Digestive
Lung
Men’s Health
Mental health
Physiotherapy
Rheumatology
Skin and hair
Sleep Disorders
Spine
Transplant
Women Health
Thyroid
Vascular Surgery
Gastric Banding
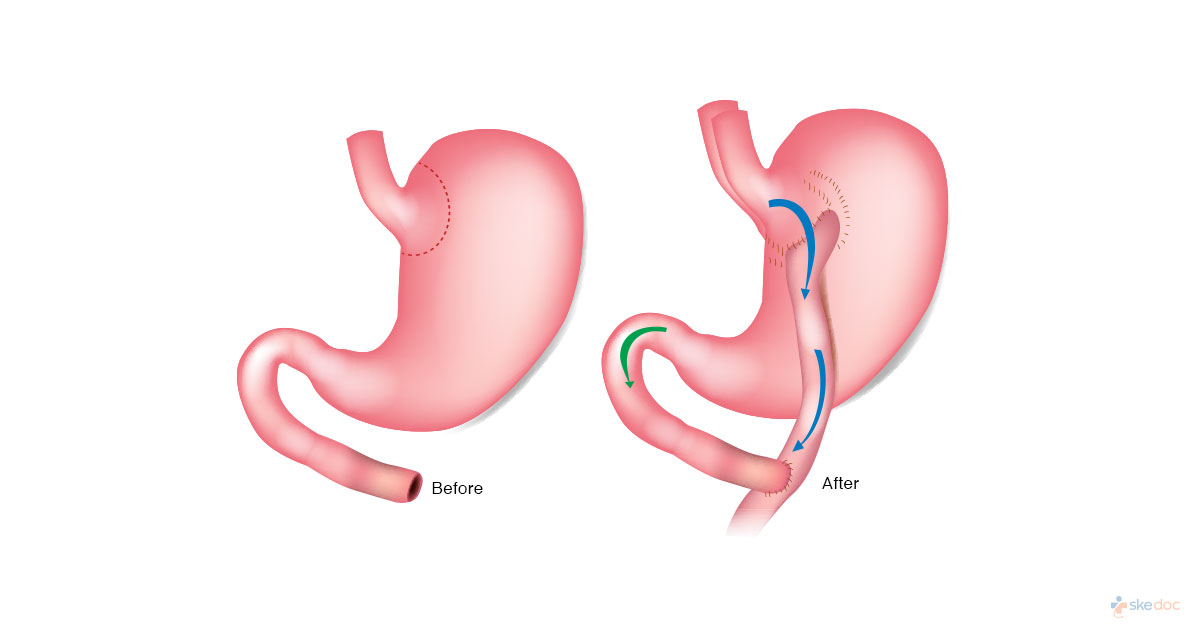
What Is Gastric Banding?
Gastric banding is a surgical procedure that is done for the management of obesity. Gastric banding is one of the many bariatric surgeries that are done for the management of obesity. Obesity is a leading cause of death worldwide, while it can be medically managed, surgical intervention ensures greater weight is lost and a lesser amount of weight is regained. In gastric banding bariatric surgery, the size of the stomach is reduced by placing an inflatable silicone device around the top part of the stomach. The smaller size of the new stomach helps to reduce the amount of food that is eaten and ensures early fullness and satiety, and the slow passage of food through the stomach.
Alternate names
- Lap band surgery
- A-band
- LABG’s
Is this procedure an elective or an emergency procedure?
Gastric banding bariatric surgery is an elective procedure.
Types of procedure
Gastric banding surgery is mostly done via the laparoscopic route and may use one of the following types of bands:
- Gastric banding with an adjustable gastric band
- Gastric banding with lap band
Indications of gastric banding
The indications for gastric banding bariatric surgery include:
- Body mass index higher than 40
- Body mass index between 35 to 40 and associated with the following:
- Severe diabetes mellitus
- Pickwickian Syndrome
- Obesity-related cardiomyopathy
- Severe sleep apnea
- Osteoarthritis that is limiting normal lifestyle
Body mass index is the relative weight for height and it also relates to the total amount of body fat that is present. It is calculated as:
Body mass index = weight in Kg/(height in meters)2
Contraindications and risk factors of gastric banding
The contraindications and risk factors for gastric bypass surgery include:
- End-stage organ disease including hepatic, cardiac, pulmonary, renal, etc.
- Psychiatric disorders
- Substance abuse
- Inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
- Cirrhosis
- Portal hypertension
- Esophageal or gastric varices
- History of gastric perforation near the site of placement of the band.
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Autoimmune connective tissue disorders.
- Congenital anomalies of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Inability or unwillingness to comply with postsurgical diet and lifestyle modifications.
Investigations before the procedure
Some investigations that are done before gastric bypass bariatric surgery include:
- Laboratory tests-
- CBP and ESR
- Liver and renal function tests
- Complete metabolic panel
- Complete urine examination
- Blood glucose/HbA1c
- Imaging tests-
- Chest x-ray
- Echocardiogram
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Assessment of body mass index
- Electrocardiography (ECG)
Preoperative advice
Before a weight loss surgery, the following are done:
- Risks and benefits of the procedure are explained.
- Liquid diet for 24 hours before the procedure.
- Nothing by mouth for 12 hours before surgery.
- Antibiotic prophylaxis may be started before the surgery.
Intraoperative Details
Duration: Gastric banding bariatric surgery can last between 1 to 3 hours depending on the type of procedure that is being.
Anesthesia: Gastric banding is generally done under general anesthesia with intubation.
Description of the procedure:
With the individual lying on his/her back, iv lines and urinary catheter are put in place, endotracheal intubation is done and after the general anesthetic has taken effect, 4 to 5 small incisions are made in the abdomen through which a fiber-optic scope and other surgical instruments are introduced after abdominal insufflation. The liver is retracted and the dissection of the gastrophrenic ligaments and a window is created near the gastrohepatic ligament. A small tunnel is then created in the retroperitoneal fat behind the stomach. A band is then passed through the tunnel and placed such that the balloon of the band is facing the stomach and the fundus of the stomach is then sutured with absorbable sutures. Exteriorization of the tubing of the band is done by clearing the connective tissue covering the abdominal muscles and the balloon is completely deflated. The surgical instruments are removed, insufflation is done, and the incisions are closed with sutures.
Postoperative details
After the gastric banding surgery, the following are done:
- The individual is moved to a recovery room and an ICU and monitored until awake and stable.
- The cardiopulmonary function is monitored.
- Extubation is done once the individual is stable.
- Early ambulation is encouraged.
Common post-procedure occurrences:
- Pain
- Nausea
- Lightheadedness and fatigue
Discharge: Usually on the 1st postoperative day if there are no complications.
Review: Usually done after 4-6 weeks for the adjustment of the gastric band by inflating the balloon with saline solution. The next adjustment is done at the end of 8 weeks after the procedure. Further adjustment s are done as required every 1-2 months until the individual is comfortable.
Role of diet/exercise/lifestyle changes
Some measures that may be taken after gastric banding surgery include:
- Avoiding strenuous activity for the first week after the procedure.
- Following the diet as advised by the physician.
- Gradually increase in physical activity as advised.
- Maintain an active lifestyle and exercise as advised to avoid weight gain.
Complications of gastric banding
Some complications that may be seen after a gastric banding surgery may include:
- Intraoperative and postoperative bleeding.
- Infections
- Pouch enlargement due to overeating, placement of the band too low on the stomach.
- Band slippage
- Band erosion
- Dilation of the esophagus
- Vomiting
- Heartburn
- Perforation of stomach
- Injury to spleen
Prognosis
The prognosis of gastric banding is good especially in young individuals with very high BMI and long-term reduction of body weight. It has been observed that the gastric band would eventually need to be removed in a lot of individuals. In comparison, gastric bypass surgery shows better long-term results and control of comorbidities.
Indications for hospitalization if required
Brief hospitalization will be required for gastric banding.
Suggested clinical specialist/Department to consult for the procedure
Gastric banding is done by specialists from the Department of Surgical Gastroenterology and Interventional Endoscopic Surgery.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo




