Allergy
Blood Diseases
Bone & Joints
Brain
Cancer
Child Care
Cosmetic Surgery
Diabetes
Endocrinology
ENT
Eye
Gen Medicine
General Surgery
Heart
Kidney
Lifestyle
Liver & Digestive
Lung
Men’s Health
Mental health
Physiotherapy
Rheumatology
Skin and hair
Sleep Disorders
Spine
Transplant
Women Health
Thyroid
Vascular Surgery
Bronchoscopy
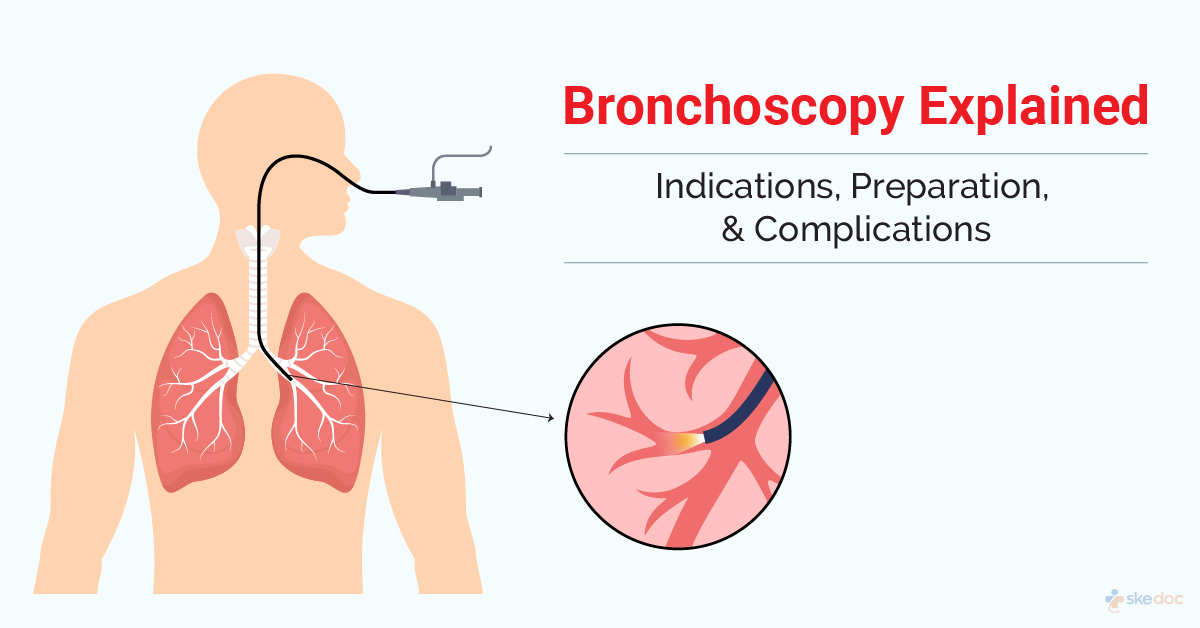
What is Bronchoscopy?
Bronchoscopy is a minimally invasive diagnostic and therapeutic procedure for evaluating and managing diseases of the lungs and the airways. The procedure is performed by pulmonologists using an endoscopic instrument called a bronchoscope that helps to visualize the insides of the lungs and the airways with the help of fiber optics and video equipment and with the use of additional instruments to collect tissue samples or remove foreign bodies.
Is a bronchoscopy procedure an elective or an emergency procedure?
Bronchoscopy is done as an elective procedure, but in certain circumstances, it may also be done as an emergency procedure.
Types
Bronchoscopy may be of the following types:
- Rigid Bronchoscopy: It is mostly employed for accessing the lower airways; it is generally used for the retrieval of inhaled foreign bodies without causing injury to the airways
- Flexible Bronchoscopy: It is the most commonly used Bronchoscopy procedure that employs an instrument with fiber optics that transmit images and helps in easy navigation through the lung's spaces and airways
Indications
Some indications for bronchoscopy include:
- Diagnostic:
- To evaluate chronic cough
- To evaluate bleeding in the lungs
- To evaluate infection of the lungs
- To evaluate the possible presence of cancer in the lungs or airways
- To obtain tissue samples from inside the lungs or airways
- Therapeutic:
- Removal of foreign bodies, secretions, or blood from the lungs and airways
- Removal of tumors
- Removal of strictures in the airways
- For placement of stents
- For percutaneous tracheostomy
- Tracheal intubation
- For the management of pneumothorax (collapsed lung)
Contraindications & Risk factors
Bronchoscopy is not done under the following circumstances:
- Presence of life-threatening arrhythmias
- Acute respiratory failure
- Severe tracheal obstruction
- History of recent myocardial infarction
- Severe bleeding disorders
Investigations before the procedure
Some investigations that may be advised before performing a Bronchoscopy include:
- CBP & ESR
- Coagulation Profile
- ECG
Preoperative advice
Before performing a bronchoscopy, the following are done:
- The risks and benefits of the procedure are explained.
- Anticoagulant medication may need to be stopped at least a few days before the procedure.
- Nothing by mouth at least 6 – 8 hours before the procedure
Intraoperative details
Anesthesia: The procedure is performed under conscious sedation and local anesthesia.
Duration: Bronchoscopy can last 3-5 hours, depending on the procedure.
Details of procedure
After the administration of sedation and local anesthetic, with the individual in either a seated or lying down position, the lubricated bronchoscope is introduced either through the nose or mouth, down the throat, through the vocal cords, and into the trachea (windpipe) and finally into the bronchi. Several other procedures, such as bronchial washing with saline, bronchial brushing to obtain suspicious cells, bronchoalveolar lavage with saline to retrieve cells proteins or microorganisms at the alveolar level, transbronchial biopsy using forceps to retrieve lung tissue, and transbronchial needle aspiration using a retractable needle to obtain samples from lymph nodes and mediastinal masses may also be done as required.
After the procedure is complete, the instrument is slowly withdrawn along the same path.
Post-operative advice
After the procedure, the individual is placed under observation and monitored for a few hours. The following are done:
- Supplemental oxygen is given for a few hours, and oxygen saturation is checked.
- Monitored for the return of gag reflux
- A Chest X-ray PA view is taken to monitor for pneumothorax if a lung biopsy was done.
- Nothing by mouth until the gag reflex returns and the individual can swallow and cough normally; starting with sips of water intake is slowly transitioned to soft foods
Common post-procedure complaints:
- Dry mouth
- Sore throat
- Cough
- Hoarseness of voice
Discharge: If recovery is complete and no complications are present, the individual is discharged on the next day after the procedure
Review: As advised by the attending specialist
Role of Diet/ Exercise/ Lifestyle changes
Some measures that need to be taken after a Bronchoscopy include:
- Getting sufficient rest
- Eating a healthy diet
Complications
Some complications associated with Bronchoscopy include:
- Minor bleeding
- Fever
- Difficulty in breathing
- Increase in cough
- Vocal cord swelling and hoarseness of voice
- Damage to the vocal cords
- Bronchospasm
- Collapsed lung (pneumothorax)
- Arrhythmias
- Myocardial infarction (rare)
Prognosis
Bronchoscopy is a relatively safe procedure, and complications are usually minimal.
When to contact the doctor or hospital?/ Indications for hospitalization if required
It is advisable to seek medical attention if there is persistent fever, an increase in chest pain, difficulty breathing, or coughing up more than 15 – 20 ml of blood.
Suggested clinical specialist/ Department to consult for this procedure
- Pulmonology
Was this article helpful?
YesNo




