Allergy
Blood Diseases
Bone & Joints
Brain
Cancer
Child Care
Cosmetic Surgery
Diabetes
Endocrinology
ENT
Eye
Gen Medicine
General Surgery
Heart
Kidney
Lifestyle
Liver & Digestive
Lung
Men’s Health
Mental health
Physiotherapy
Rheumatology
Skin and hair
Sleep Disorders
Spine
Transplant
Women Health
Thyroid
Vascular Surgery
Blepharitis
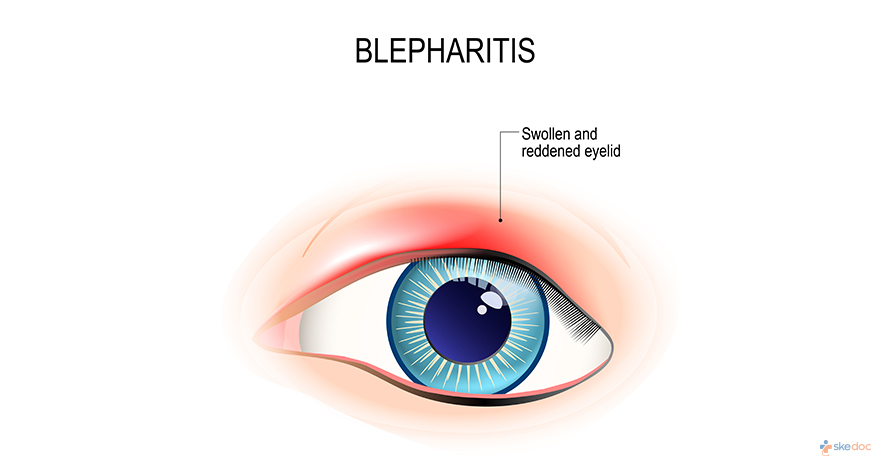
What is Blepharitis?
Blepharitis, also known as eyelid inflammation, is an inflammatory disease affecting the eyelids and results most commonly when the oil glands at the base of the eyelids become clogged. It can be a long-standing condition and is not contagious. It can affect individuals of any age but is more common in the age group of 50 years and above.
Is Blepharitis condition a Medical emergency?
Blepharitis is not a medical emergency.
Types
Blepharitis may be of the following types:
- Anterior Blepharitis: It affects the skin, eyelashes, and lash follicles
- Staphylococcal variant: It is caused by infection with the Staphylococcus bacterium
- Seborrheic variant: It is caused due to clogging of the oil glands
- Posterior Blepharitis: It affects the meibomian glands and openings, tarsal plate, and the junction of the eyelids and the conjunctiva
Causes
Blepharitis is caused when there is a growth of bacteria in the eyelids leading to invasion of the tissues, immune system reaction and damage, damage to the tissues from bacterial toxins and waste products. Bacterial growth in the eyelids is seen when there are conditions like seborrheic dermatitis or dysfunction of the meibomian glands. It is also common in individuals who do not practice good hand or eyelid hygiene.
Risk factors
Factors that increase the risk of Blepharitis include the following:
- Age: Older than 50 years
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Acne rosacea
- Atopic dermatitis
- Dry eye syndrome
- Chalazion
- Trichiasis
- Ectropion or Entropion
- Conjunctivitis
- Keratitis
- Autoimmune diseases such as SLE
- Improper diet and poor nutrition
Symptoms & signs
The signs and symptoms of Blepharitis may include the following:
- Watering of eyes
- Redness of eyes
- Swelling of eyelids
- Presence of crusts at the corners of the eyelids, which is usually worse on waking up
- Sticking of eyelids
- Flaking of skin on the eyelids
- Foreign body sensation: More in posterior Blepharitis
- Loss of eyelashes
- Blurring on vision
- Photophobia: Extreme sensitivity to light
- Excessive blinking
Investigations
Some investigations that may be advised for the evaluation of Blepharitis include:
- Laboratory tests:
- Tear film testing
- Culture and sensitivity test from eyelids margins
- Microscopic evaluation of eyelashes
- Imaging tests: Not usually done:
- Lipview
- Keratography
- Complete ophthalmic examination
Diagnosis
A diagnosis of Blepharitis is established based on medical history, clinical evaluation, and results of the investigations done.
Treatment options
In a majority of cases of Blepharitis, simple hygiene and self-care measures can help to treat the condition. Long-standing cases and complications may require medical and surgical management.
Medical management
Medical management of Blepharitis may include the following:
- Antibiotics: Long term course of antibiotics such as tetracycline for Blepharitis not responding to conservative management or if conjunctivitis is present
- Artificial tear solutions or ointments: If there is tear film dysfunction
- Selenium shampoo: For the management of seborrheic dermatitis
- Topical corticosteroids: If atopic dermatitis or corneal infiltrates are present
Interventional including surgery and indications for surgery
Surgical interventions are needed only for the management of complications that develop due to Blepharitis. Surgical interventions may include:
- Chalazion treatment procedures
- Oculoplastic surgical procedures for the management of entropion or ectropion
- Epilation: For trichiasis
- Laser or cryotherapy: For trichiasis
Role of diet/ Exercise/ Lifestyle changes/ Preventive measures
Some measures that can be taken for the prevention and management of Blepharitis include:
- Warm compression on eyelids
- Proper washing of the eyelids
- Maintaining proper eyelid hygiene and hand hygiene
- Avoiding rubbing and frequently touching the eyes and eyelids
- Taking measures to avoid dandruff and mite infections
Complications
Some complications associated with Blepharitis include:
- Entropion: The inward turning of the eyelids
- Ectropion: The outward turning of the eyelids
- Loss of eyelashes
- Keratitis: Inflammation of the cornea
- Corneal ulceration
- Conjunctivitis: Inflammation of the conjunctiva
- Ulceration of the eyelids
- Trichiasis and lid notching
- Complications of steroid therapy: Such as cataract, glaucoma, viral infections
Prognosis
The prognosis for Blepharitis is generally very good and a majority of the cases respond to simple eye care measures and lid hygiene. The condition may become chronic in a few individuals with periods of remission and exacerbation. In a few individuals, long-standing Blepharitis can lead to serious complications such as corneal ulceration and keratitis.
When to contact the doctor or hospital?/ How to identify the emergency or complications?
It is advisable to seek medical attention if the signs and symptoms of Blepharitis are noticed.
Indications for hospitalization if required
Hospitalization is not required for the management of Blepharitis. Brief hospitalization may be required if surgical interventions are required for the management of complications.
Suggested clinical specialist/ Department to consult for this condition
- Ophthalmology
Was this article helpful?
YesNo




