Allergy
Blood Diseases
Bone & Joints
Brain
Cancer
Child Care
Cosmetic Surgery
Diabetes
Endocrinology
ENT
Eye
Gen Medicine
General Surgery
Heart
Kidney
Lifestyle
Liver & Digestive
Lung
Men’s Health
Mental health
Physiotherapy
Rheumatology
Skin and hair
Sleep Disorders
Spine
Transplant
Women Health
Thyroid
Vascular Surgery
Cataract
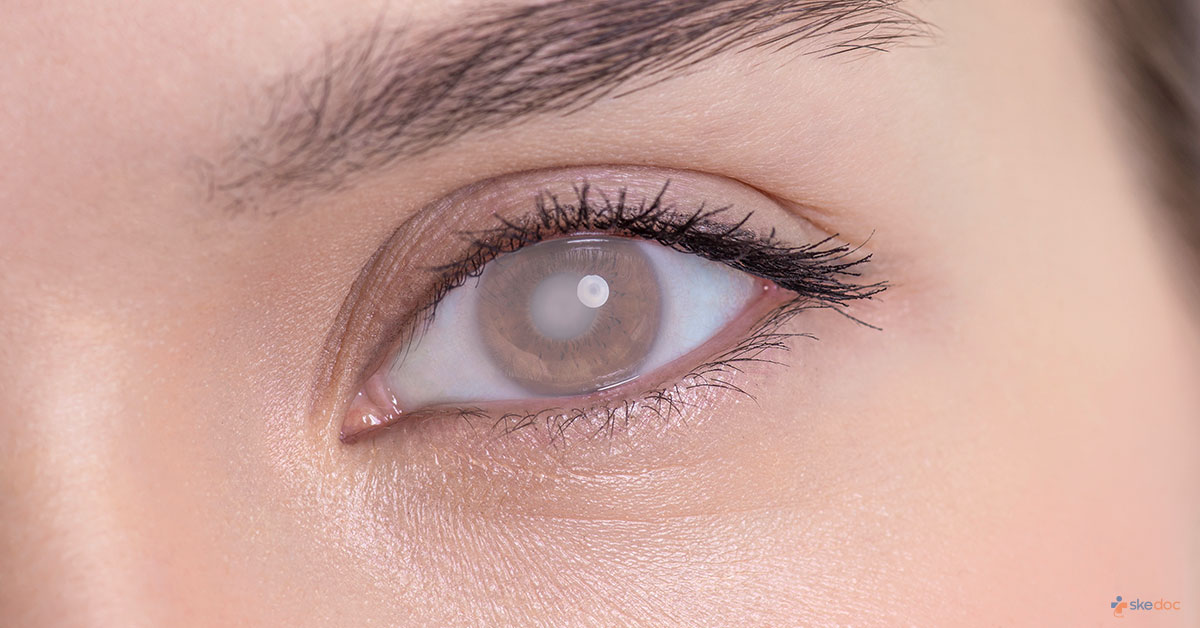
What Is A Cataract?
A Cataract is defined as a thick, cloudy area that develops in the eye's lens and is one of the most common conditions affecting the eye. It develops slowly and can affect either one or both eyes, and as it progresses, it interferes with normal vision.
Is Cataract a Medical Emergency?
A Cataract is rarely a medical emergency.
Types
The types are classified depending on the part of the lens they affect, and they are
- Nuclear Cataracts: This is the most common type; it affects the central part of the lens. As the nuclear cataract advances, it is called a brunescent (very hard/stony) cataract.
- Cortical Cataracts: These affect the edges of the lens. They form wedge-shaped streaks at the edges. These streaks gradually progress towards the centre.
- Posterior Subcapsular Cataracts: This cataract affects the back of the natural lens. It grows faster and causes early vision impairments.
- Congenital Cataracts: These are present at birth and gradually develop in early childhood. They may be due to genetic reasons, intrauterine infections, or trauma.
Causes
The following are the causes:
- Advanced age
- Trauma to the eye
- Prior eye surgery
- Radiation exposure
- Other underlying medical conditions like diabetes, glaucoma, etc
- Long-term use of corticosteroids or other medications
- Smoking tobacco
- Genetic factors
Risk Factors
Factors that influence the development of cataracts include the following:
- Smoking tobacco
- Alcohol consumption
- Prolonged exposure to sunlight
- High blood pressure
- Eye injury or trauma
- Prior eye surgery
- Long-term use of corticosteroids or other medications
- Exposure to radiation
Signs & Symptoms
Signs and symptoms include the following:
- Blurred or double vision
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Difficulty seeing bright lights
- Seeing halos around the light
- Fading of colours
- Decrease vision with spectacles/contact lenses
Investigations
Investigation tests that are performed to rule out cataracts include the following:
- Visual acuity test: An eye chart consists of a series of letters placed size-wise. An individual is made to read the letters with one eye closed. This test detects any vision impairments
- Slit-lamp examination: A slit-lamp is an instrument that provides a magnifying view of the eye structures, such as the eyelid, sclera, conjunctiva, iris, and cornea. It is used to detect abnormalities
- Tonometry: This procedure is performed to measure the pressure inside the eye.
- An ophthalmoscope is used to observe the internal parts of the eye, the retina, and the optic nerve. Tests are also performed to check the sensitivity to glare and perception of colours
- Biometry: To measure the eye parameters that facilitate the planning for surgery
- Tomography: To measure the cornea, which is a crucial part of predicting better results after surgery
- Optical Coherence Tomography: To measure the thickness of the retina to r/o any retinal disease before surgery
- Dry Eye Assessment: At times, dry eye can be aggravated after cataract surgery, so it is important to diagnose and treat the same before surgery
Diagnosis
A diagnosis is made based on medical history, clinical evaluation, and investigation results.
Stages
Cataracts are divided into four stages depending upon the severity of the condition. They are as follows:
- Early Cataract: This is the initial stage where slight blurring and foggy vision begin
- Immature Cataract: Yellow-colour deposits start to accumulate in the lens. The clouding of the lens begins to develop in the centre
- Mature Cataract: The cloudy area increases gradually, giving a milky white appearance. It spreads to the edges of the lens and interferes with the vision
- Hypermature Cataract: The Cataract becomes very dense and complex with significant vision impairment
Treatment Options
Medical Treatment
Apart from surgery, the treatment may include prescribing magnifying lenses or stronger eyeglasses.
Interventional Treatment Including Surgery And Indications For Surgery/ Surgical Treatment
Surgery is the primary treatment for cataracts. The cloudy lens is replaced with an artificial lens. Surgery is performed when cataracts interfere with daily activities of life. Surgery can be performed at any stage of the cataract.
Different methods of the surgery are as follows:
- Femtosecond Laser-Assisted Cataract Surgery (FLACS): Laser is used to assist in cataract surgery. This helps in increasing precision and quicker recovery. This is a highly customizable procedure.
- Phacoemulsification: This is a widely used cataract procedure. Ultrasound waves are used to break down the cataract into tiny fragments and then remove it from the eye.
- Extracapsular Cataract Extraction (ECCE): In this procedure, the cataract is removed manually through a long incision in the cornea and followed by stitches.
- Manual small incision Cataract surgery (MSICS): This form of ECCE surgery is done with a small incision.
- Intracapsular Cataract Extraction (ICCE): In this surgery, the lens and lens capsule are removed in one piece. This surgery is rarely performed due to its high rate of complications.
Cataract surgery is very safe and gives good outcomes. Surgery is done on an outpatient basis.
Role Of Diet/ Exercise/ Lifestyle Changes/ Preventive Measures
The following measures can prevent the development of Cataracts:
- Wearing sunglasses to protect against ultraviolet rays from the sun
- Smoking cessation
- Maintaining adequate weight
- A healthy diet with vitamins A, C, and E.
- Regular eye checkups
- Keeping diabetes in control and managing other health problems
- Limiting alcohol consumption
Complications
Cataracts may not be problematic initially, but they can cause complications as they progress. Some of them include the following:
- Visual impairments like blurred and foggy vision
- Having trouble with reading and driving
- Complications after the surgery include an increased risk of retinal detachment, endophthalmitis, corneal edema, and posterior capsular opacification.
Prognosis
The overall prognosis of cataracts is very good.
Can we have spectacle independence after cataract surgery?
Yes, premium artificial lenses like the trifocal and extended vision lenses do assist in providing all ranges of vision. The need for spectacles for various activities decreases significantly. Please check with your doctor if you are suitable for the same.
When to contact the doctor? / How to identify the complications?
A medical consultation is warranted if vision changes, eye pain, headaches, and sensitivity to light are noticed.
Indications for hospitalization, if required
Hospitalization is not required for the management of cataracts or surgeries in a majority of cases.
Suggested clinical specialists/ Department to consult for this condition
- Ophthalmology
- Cataract surgeon
Was this article helpful?
YesNo
Comments





